zarizeni:esp8266
Obsah
ESP8266
Příklad jak naprogramovat ESP8266 v Arduino IDE od mikroma.
Web autora příkladů: https://mikrom.cz/
Kontakt na autora: mikrom@mikrom.cz
Nezapomeňte na začátku kódu nastavit své správné proměnné (SSID vlastní wifi, heslo k wifi síti, správnou adresu serveru a GUID vyplněné v administraci na tmep.cz).
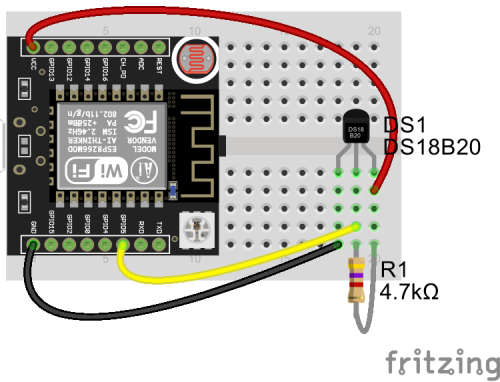
Teplota
- tmep_send_temperature.ino
/* Simple sketch for sending data to the TMEP.cz by mikrom (http://www.mikrom.cz) http://wiki.tmep.cz/doku.php?id=zarizeni:esp8266 If you send only temperature url will be: http://ahoj.tmep.cz/?mojemereni=25.6 (domain is "ahoj" and guid is "mojemereni" If you send also humidity url will be: http://ahoj.tmep.cz/?mojemereni=25.6&humV=60 But for humidity You will need DHT11 or DHT22 sensor and code will need some modifications, see the other sketch. Blinking with ESP internal LED according status: LED constantly blinking = connecting to WiFi LED on for 5 seconds = boot, setup, WiFi connect OK LED blink 2x per second = temp error (wrong pin, bad sensor, read -127.00°C) LED blink 3x per second = connect to host failed LED blink 4x per second = client connection timeout LED blink 1x per [sleep] = send data ok */ #include <ESP8266WiFi.h> // WiFi library #include <OneWire.h> // OneWire communication library for DS18B20 #include <DallasTemperature.h> // DS18B20 library // Define settings const char ssid[] = "---ssid---"; // WiFi SSID const char pass[] = "---password---"; // WiFi password const char domain[] = "---domain---"; // domain.tmep.cz const char guid[] = "---guid---"; // mojemereni const byte sleep = 1; // How often send data to the server. In minutes const byte oneWireBus = 5; // Pin where is DS18B20 connected // Create Temperature object "sensors" OneWire oneWire(oneWireBus); // Setup a oneWire instance to communicate with any OneWire devices (not just Maxim/Dallas temperature ICs) DallasTemperature sensors(&oneWire); // Pass our oneWire reference to Dallas Temperature. void setup() { pinMode(2, OUTPUT); // GPIO2, LED on ESP8266 // Start serial Serial.begin(115200); delay(10); Serial.println(); // Connect to the WiFi Serial.print(F("Connecting to ")); Serial.println(ssid); WiFi.begin(ssid, pass); while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) { digitalWrite(2, LOW); delay(100); digitalWrite(2, HIGH); // Blinking with LED during connecting to WiFi delay(500); //digitalWrite(2, HIGH); // Blinking with LED during connecting to WiFi Serial.print(F(".")); } Serial.println(); Serial.println(F("WiFi connected")); Serial.print(F("IP address: ")); Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); Serial.println(); sensors.begin(); // Initialize the DallasTemperature DS18B20 class (not strictly necessary with the client class, but good practice). // LED on for 5 seconds after setup is done digitalWrite(2, LOW); delay(5000); digitalWrite(2, HIGH); } void loop() { sensors.requestTemperatures(); // Send the command to get temperatures. request to all devices on the bus float t = sensors.getTempCByIndex(0); // Read temperature in "t" variable if (t == -127.00) { // If you have connected it wrong, Dallas read this temperature! :) Serial.println(F("Temp error!")); // Blink 2 time when temp error digitalWrite(2, LOW); delay(100); digitalWrite(2, HIGH); delay(100); digitalWrite(2, LOW); delay(100); digitalWrite(2, HIGH); delay(1000); return; } // Connect to the HOST and send data via GET method WiFiClient client; // Use WiFiClient class to create TCP connections char host[50]; // Joining two chars is little bit difficult. Make new array, 50 bytes long strcpy(host, domain); // Copy /domain/ in to the /host/ strcat(host, ".tmep.cz"); // Add ".tmep.cz" at the end of the /host/. /host/ is now "/domain/.tmep.cz" Serial.print(F("Connecting to ")); Serial.println(host); if (!client.connect(host, 80)) { // If you didn't get a connection to the server Serial.println(F("Connection failed")); // Blink 3 times when host connection error digitalWrite(2, LOW); delay(100); digitalWrite(2, HIGH); delay(100); digitalWrite(2, LOW); delay(100); digitalWrite(2, HIGH); delay(100); digitalWrite(2, LOW); delay(100); digitalWrite(2, HIGH); delay(1000); return; } Serial.println(F("Client connected")); // Make an url. We need: /?guid=t String url = "/?"; url += guid; url += "="; url += t; Serial.print(F("Requesting URL: ")); Serial.println(url); // Make a HTTP GETrequest. client.print(String("GET ") + url + " HTTP/1.1\r\n" + "Host: " + host + "\r\n" + "Connection: close\r\n\r\n"); // Blik 1 time when send OK digitalWrite(2, LOW); delay(100); digitalWrite(2, HIGH); // Workaroud for timeout unsigned long timeout = millis(); while (client.available() == 0) { if (millis() - timeout > 5000) { Serial.println(F(">>> Client Timeout !")); client.stop(); // Blink 4 times when client timeout digitalWrite(2, LOW); delay(100); digitalWrite(2, HIGH); delay(100); digitalWrite(2, LOW); delay(100); digitalWrite(2, HIGH); digitalWrite(2, LOW); delay(100); digitalWrite(2, HIGH); delay(100); digitalWrite(2, LOW); delay(100); digitalWrite(2, HIGH); delay(1000); return; } } Serial.println(); // Wait for another round delay(sleep*60000); }
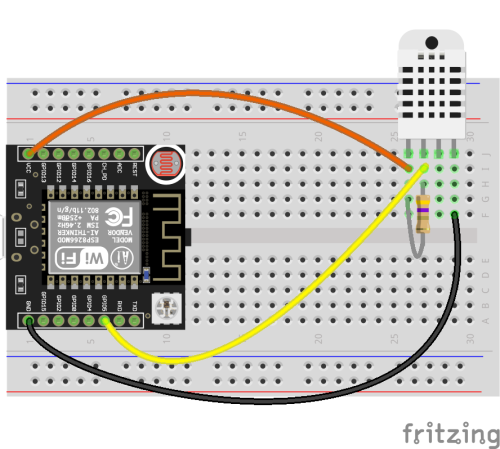
Teplota a vlhkost
- tmep_send_temperature_and_humidity.ino
// Simple sketch for sending data to the TMEP.cz // by mikrom (http://www.mikrom.cz) // http://wiki.tmep.cz/doku.php?id=zarizeni:esp8266 // // If you send only temperature url will be: http://ahoj.tmep.cz/?mojemereni=25.6 (domain is "ahoj" and guid is "mojemereni" // If you send also humidity url will be: http://ahoj.tmep.cz/?mojemereni=25.6&humV=60 // but for humidity You will need DHT11 or DHT22 sensor and code will need some modifications // // Not tested, but should work! :) #include <ESP8266WiFi.h> // WiFi library #include "DHT.h" // DHT sensor library // Define settings const char* ssid = "---wifi ssid---"; // WiFi SSID const char* pass = "---wifi pass---"; // WiFi password const char* domain = "---domain---"; // domain.tmep.cz const char* guid = "---guid---"; // mojemereni const long sleep = 600000; // How often send data to the server. Default is 600000ms = 10 minute const byte dhtPin = 5; // Pin where is DHT connected const byte dhtType = 22; // DHT type, for DHT11 = 11, for DHT22 = 22 DHT dht(dhtPin, dhtType); // Initialize DHT sensor. void setup() { // Start serial Serial.begin(115200); delay(10); Serial.println(); // Connect to the WiFi Serial.print("Connecting to "); Serial.println(ssid); WiFi.begin(ssid, pass); while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) { delay(500); Serial.print("."); } Serial.println(); Serial.println("WiFi connected"); Serial.print("IP address: "); Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); Serial.println(); dht.begin(); // Initialize the DHT sensor delay(10000); } void loop() { // Reading temperature or humidity takes about 250 milliseconds! // Sensor readings may also be up to 2 seconds 'old' (its a very slow sensor) float h = dht.readHumidity(); // Read temperature as Celsius (the default) float t = dht.readTemperature(); // Check if any reads failed and exit early (to try again). if (isnan(h) || isnan(t)) { Serial.println("Failed to read from DHT sensor!"); return; } // Connect to the HOST and send data via GET method WiFiClient client; // Use WiFiClient class to create TCP connections char host[50]; // Joining two chars is little bit difficult. Make new array, 50 bytes long strcpy(host, domain); // Copy /domain/ in to the /host/ strcat(host, ".tmep.cz"); // Add ".tmep.cz" at the end of the /host/. /host/ is now "/domain/.tmep.cz" const int httpPort = 80; Serial.print("Connecting to "); Serial.println(host); if (!client.connect(host, httpPort)) { // If you didn't get a connection to the server Serial.println("Connection failed"); return; } Serial.println("Client connected"); // Make an url. We need: /?guid=t&humV=h String url = "/?"; url += guid; url += "="; url += t; url += "&humV="; url += h; Serial.print("Requesting URL: "); Serial.println(url); // Make a HTTP GETrequest. client.print(String("GET ") + url + " HTTP/1.1\r\n" + "Host: " + host + "\r\n" + "Connection: close\r\n\r\n"); // Workaroud for timeout unsigned long timeout = millis(); while (client.available() == 0) { if (millis() - timeout > 5000) { Serial.println(">>> Client Timeout !"); client.stop(); return; } } Serial.println(); // Wait for another round delay(sleep); }